Use Blockchain For Cybersecurity
Knowing that nobody can be trusted, we have built various institutions and created rules that are supposed to help us communicate in a way that can provide a certain level of security over personal paranoia. But then, courts still exist; therefore, the problem does, too.
Take into consideration the fact that what we know about blockchain is knowledge accumulated in just over 10 years of selective use. Still, many would mistakenly regard it as if it were solely related to cryptocurrency, and fail to see the full potential it offers. Victor S. knows where the best fruits are hidden.
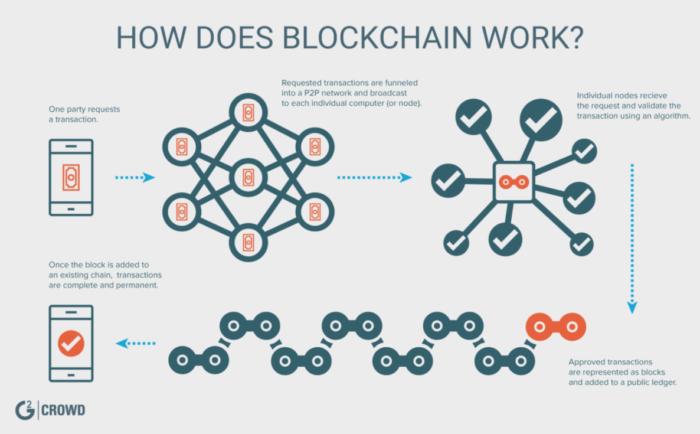
How Can Blockchain Help Boost Security?
Blockchain features that contribute to the highest level of security are based on the following:
- the distributed ledger
- the consensus aspect
- heavy encryption
To Secure, You Encrypt
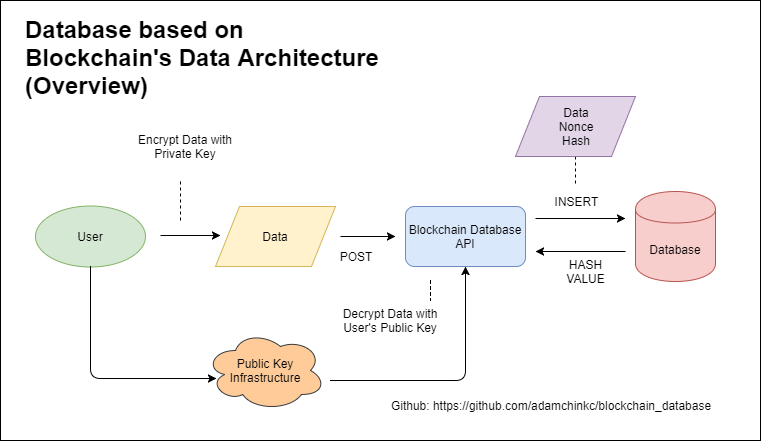
Thanks to mathematically-proven computer algorithms, blockchain could let one forget about the problems of weak passwords and compromised or stolen data.
Because it is quite plastic, blockchain can be used to boost cybersecurity in practically any case you can think of, simply by eliminating what causes the greatest number of failures: the human factor. Writing a smart contract for an ICO can contribute extensively to this new and heightened degree of security. If well-constructed, a project powered by self-executing contracts offers a great experience on the level of both security and verifiability.
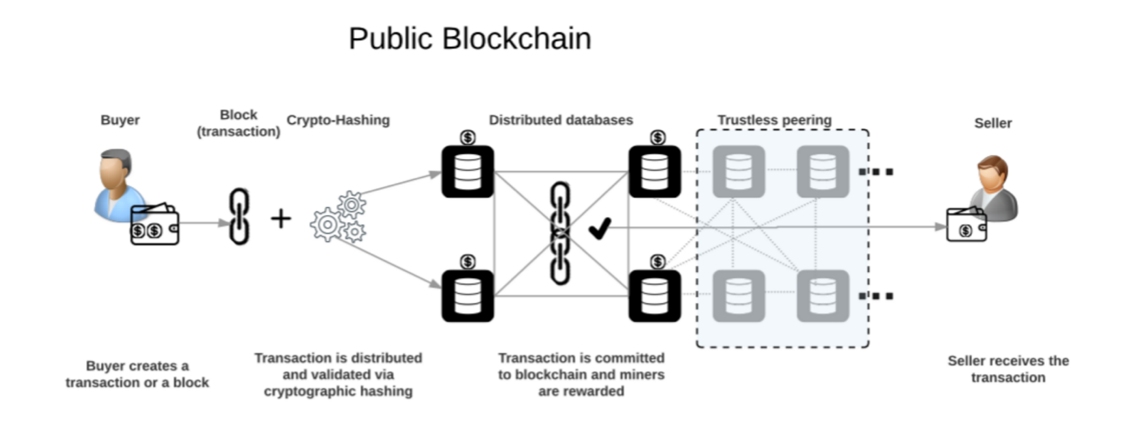
Consensus: Public and Private Blockchain
In a public blockchain, all participants can be responsible for storing data and verifying transactions.
In a private blockchain, the task of verifying transactions is laid upon a selected group of nodes rather than all users. To be able to join a private network, a user would need to be invited by an existing participant, or be one of the group of “the chosen” from the start of the network.
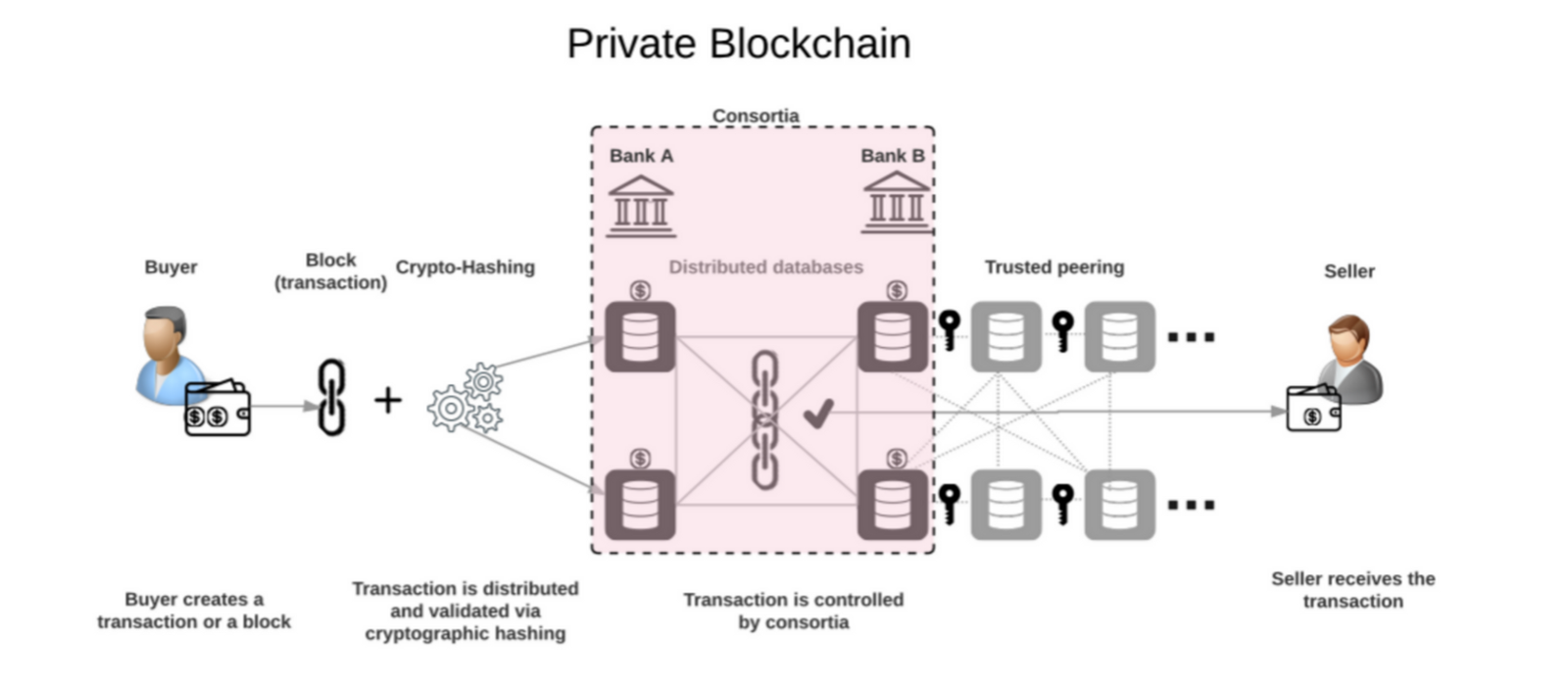
Even though a private network is not as democratic and open for everyone as a public one, it can be a great first step toward adoption of a fully decentralized model.
Decentralization and Its Share of the Security Aspect
In the world of humans, trust issues have not yet been eliminated, and therefore, technology exists in a constant loop of opposition where to every action there is a counteraction. To escape this, you have to solve a fundamental issue and then slightly change the course so that to postpone the failure day.
One existing problem is a denial-of-service attack, a very obvious counteraction to any centralized system that has shown us how far from perfection the way we store and communicate data online really is. Doing the counteraction, the distributed and decentralized nature of blockchain leaves DDoS attackers no chance, as it is next to impossible to attack all nodes simultaneously.
The Application of Blockchain
Interacting online is not always safe for the regular user, and it’s sometimes even dangerous if you have a business running on an internet platform.

In 2018, technology has already developed into a whole separate world. It has touched and influenced every aspect of real life, turning internet- and technology-based reality into a much simpler and more organized process.
If you think about it, all kinds of real-world services are represented in the cyber world, and very often, it is technology that offers a much better experience. With blockchain in use, who knows what new applications are yet to be discovered?












